Route Management
Pure Dev provides a powerful visual interface for managing API routes, combined with a type-safe runtime for handling requests and responses.
Abstraction Layer
While Pure Dev is built on top of Hono, we provide a powerful abstraction layer through the Pure object. This abstraction:
- Provides a consistent, type-safe API for your routes
- Simplifies common operations
- Ensures forward compatibility if we change the underlying engine
- Adds Pure Dev-specific features and optimizations
// ❌ Avoid direct Hono usage
import { Hono } from 'hono'
const app = new Hono()
app.get('/users', (c) => {
return c.json({ users: [] })
})
// ✅ Use Pure Dev's abstraction
export async function handler(pure: Pure): Promise<PureResponse> {
return pure.json({
users: []
})
}
While Hono's documentation is an excellent resource for understanding HTTP concepts and patterns, we recommend using Pure Dev's abstraction layer for:
- Future-proofing your code
- Accessing Pure Dev-specific features
- Maintaining consistency across your codebase
You can still reference Hono's documentation for:
- Understanding HTTP concepts
- Learning about routing patterns
- Exploring middleware patterns
- Understanding web standards
Visual Route Management
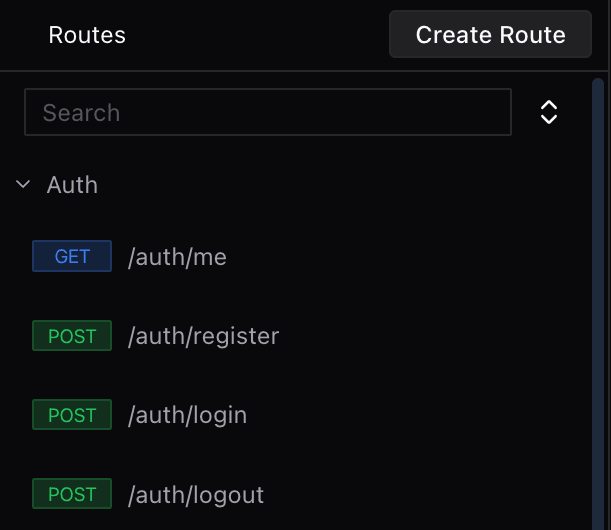
The Route Navigator provides a visual interface for:
- Creating and organizing routes
- Configuring route parameters
- Managing middleware
- Testing endpoints
Request Parameters
Pure Dev supports four types of request parameters:
Path Parameters

Path parameters are automatically detected from your route definitions and provide type-safe access:
// Route: /users/:id/posts/:postId
export async function handler(pure: Pure): Promise<PureResponse> {
const { id, postId } = pure.req.params;
// Both id and postId are fully typed
}
Body Parameters
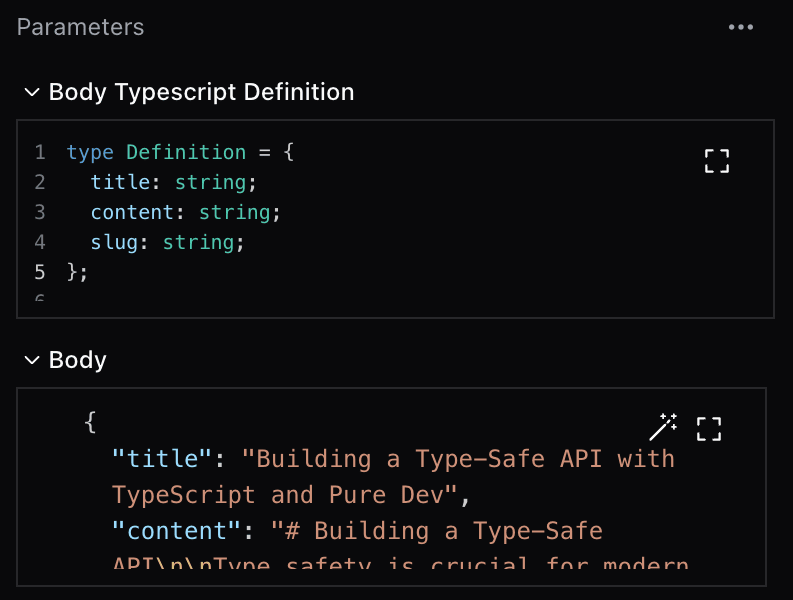
Access typed request bodies:
interface CreateUserBody {
name: string;
email: string;
}
export async function handler(pure: Pure<{ Json: CreateUserBody }>): Promise<PureResponse> {
const { name, email } = pure.req.body;
// name and email are fully typed
}
Query Parameters
Access URL query parameters with full type safety:
interface UserQueries {
page?: number;
limit?: number;
}
export async function handler(pure: Pure<{ Queries: UserQueries }>): Promise<PureResponse> {
const { page = 1, limit = 10 } = pure.req.queries;
// page and limit are fully typed
}
Headers
Access request headers with type safety:
interface CustomHeaders {
'x-api-key': string;
}
export async function handler(pure: Pure<{ Headers: CustomHeaders }>): Promise<PureResponse> {
const apiKey = pure.req.headers['x-api-key'];
// apiKey is fully typed
}
Middleware Management
Pure Dev provides a visual interface for managing middleware execution:
- Attach middleware to specific routes or globally
- Configure middleware execution order
- Exclude middleware from specific routes
- Prioritize middleware execution
Example middleware:
export async function authMiddleware(pure: Pure): Promise<void> {
const apiKey = pure.req.headers['x-api-key'];
if (!apiKey) {
throw pure.Error({
message: 'API key required',
status: 401
});
}
}
Response Handling
Pure Dev provides several methods for sending responses:
JSON Response
export async function handler(pure: Pure): Promise<PureResponse> {
return pure.json({
status: "success",
data: { id: 1, name: "John" }
}, 200);
}
Error Response
export async function handler(pure: Pure): Promise<PureResponse> {
return pure.error({
message: "Resource not found"
}, 404);
}
Other Response Types
// Text response
pure.text("Hello, World!");
// HTML response
pure.html("<h1>Hello</h1>");
// Redirect
pure.redirect("/new-location");
// Stream response
pure.streamSSE(async (emit) => {
await emit({ data: "update" });
});
The Pure Object
The pure object provides a comprehensive API for handling requests and responses:
interface IPure<PureContext> {
// Request access
req: IPureRequest<
PureContext['Json'], // Body type
PureContext['Headers'], // Headers type
PureContext['Queries'], // Query parameters type
PureContext['Params'] // Path parameters type
>;
// Database access
db: PureContext['Database'];
// Cookie management
getCookie(key: string): string | undefined;
setCookie(name: string, value: string, options?: IPureCookieOptions): void;
deleteCookie(name: string, option?: IPureCookieOptions): void;
// Variable storage
set(key: string, value: unknown): void;
var: PureContext['Variables'];
// Response methods
status(code: number): void;
json<T>(data: T, status?: number, headers?: Record<string, string>): PureResponse;
error<T>(data: T, status?: number, headers?: Record<string, string>): PureResponse;
text(data: string, status?: number, headers?: Record<string, string>): PureResponse;
html(data: string, status?: number, headers?: Record<string, string>): PureResponse;
redirect(url: string, status?: number): PureResponse;
streamSSE(cb: SSECallback): PureResponse;
}
Request Interface
The request object provides access to all request data:
interface IPureRequest<JSON, Headers, Queries, Params> {
// Request data
body: JSON;
headers: Headers;
queries: Queries;
params: Params;
// Request metadata
method: string;
url: string;
path: string;
// Body parsing methods
blob(): Promise<Blob>;
text(): Promise<string>;
arrayBuffer(): Promise<ArrayBuffer>;
formData(): Promise<FormData>;
raw(): Promise<Request>;
}
Best Practices
-
Type Safety
- Always define types for request bodies, queries, and parameters
- Use the Pure context generics for full type safety
- Let TypeScript help catch errors early
-
Middleware Organization
- Keep middleware focused and composable
- Use the visual interface to manage execution order
- Consider performance implications of middleware order
-
Error Handling
- Use
pure.error()for consistent error responses - Include appropriate HTTP status codes
- Provide helpful error messages
- Use
-
Response Format
- Be consistent with response structures
- Include status information in responses
- Set appropriate content-type headers
Next Steps
- Learn about Database Integration
- Explore Environment Management
- Set up Custom Domains